
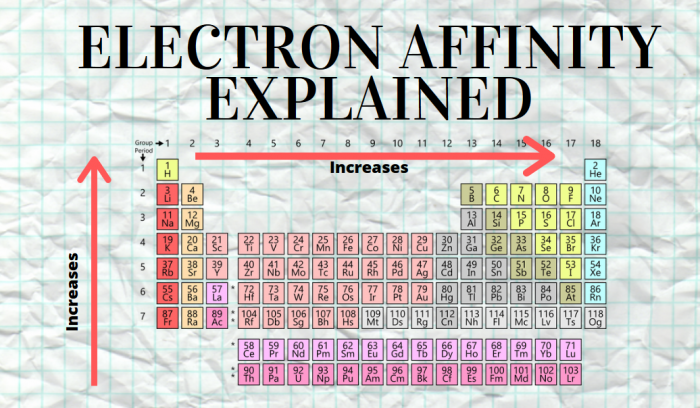
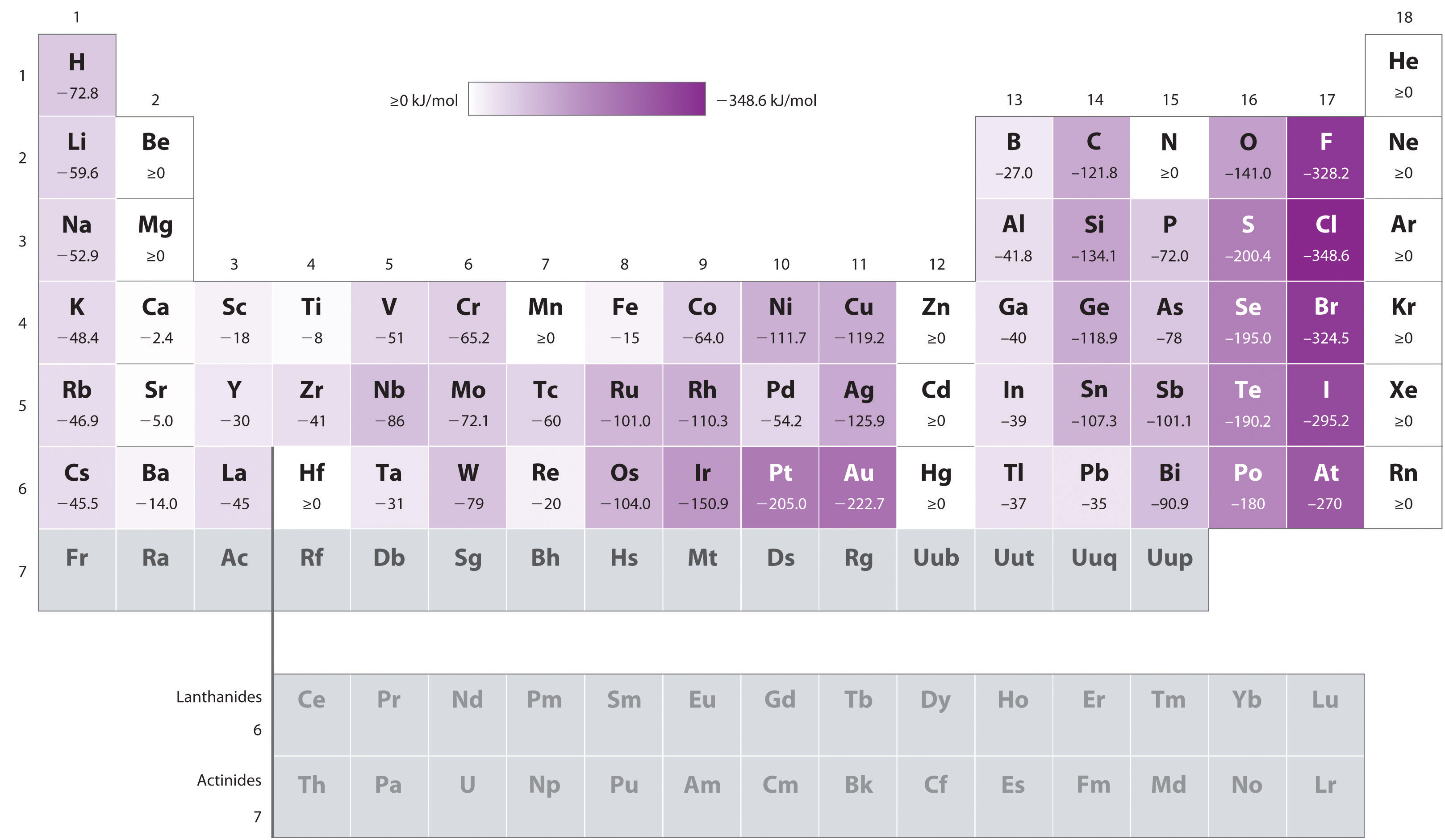
When they gain the electrons, they use energy, which allows the ion to become more stable The outer electrons experience less of a positive charge as you go across a period (effective nuclear charge)ĩ Units of EA KJ/Mol ** electron affinity is negativeġ0 Exceptions. The octet rule states that atoms with close to full valence shells will tend to gain electrons. Electrons are added increasingly farther from the nucleus, so the attractive force between the nucleus and electrons decreases The outer electrons experience less of a positive charge as you go up the periodic table (effective nuclear charge)Įlectron affinity increases as it goes across a periodħ This is because. The larger the affinity of an atom for an electron, the more negative the value Electron affinity trends are related to the trends of ionization energy because both represent the energy involved in the gain or loss of an electron by an atom, respectivelyĮlectron affinity decreases as it goes down a columnĥ This is because. is defined as the energy process in which an electron is acquired by the atom in the gas phaseģ More info. Analogically, it is possible to define the electron affinity for chemical compounds (molecules).2 Electron affinity.Electronic affinity is measured (or calculated theoretically) for isolated atoms in gaseous state.This is the case, for example, in the case of sodium-chlorine (Na-Cl) bonding in sodium chloride. When this difference is large enough, the electron is virtually transferred from one atom to the other creating an ionic bond. When two atoms form a chemical compound, the electron cloud is shifted towards the element with a higher electron affinity.However, it may be slightly different for individual isotopes. Electronic affinity is a property specific to a given element.Such calculations can be made using quantum chemistry methods.




 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
